
The WDM multiplexer is at the heart of the operation, gathering all data streams together to be transported simultaneously over a single fiber.Įarly WDM systems were able to transport two bi-directional channels over a pair of fibers. At the other end of the fiber the streams are demultiplexed, i.e. The multiplexer is at the heart of the operation, gathering all the data streams together to be transported simultaneously over a single fiber. The WDM multiplexer, sometimes referred to as the passive mux, is the key to optimizing, or maximizing, the use of the fiber. Multiplexers optimizing the use of fiber channels Since each channel is transparent to the speed and type of data, any mix of SAN, WAN, voice and video services can be transported simultaneously over a single fiber or fiberpair. It also allows new channels to be connected as needed, without disrupting the existing traffic services. Creating virtual fiber channels in this way means that the number of fibers required are reduced by the factor of the wavelengths used. All WDM wavelengths are therefore independent. Due to the physical properties of light, channels cannot interfere with each other. Each data stream is converted into a signal with a light wavelength that is a unique color. Transceivers are wavelength-specific lasers that convert data signals from SAN and IP switches to optical signals that can be transmitted into the fiber.

Transceivers – transmitting data as light In its simplest form WDM systems consist of four elements: So using an existing fiber to transport multiple traffic channels can generate substantial savings. Fiber rental or purchase represents a significant share of networking costs. In this way WDM increases the bandwidth and maximizes the usefulness of fiber. Instead of using multiple fibers for each and every service, a single fiber can be shared for several services. By allowing different light channels, each with a unique wavelength, to be sent simultaneously over an optical fiber network a single virtual fiber network is created.
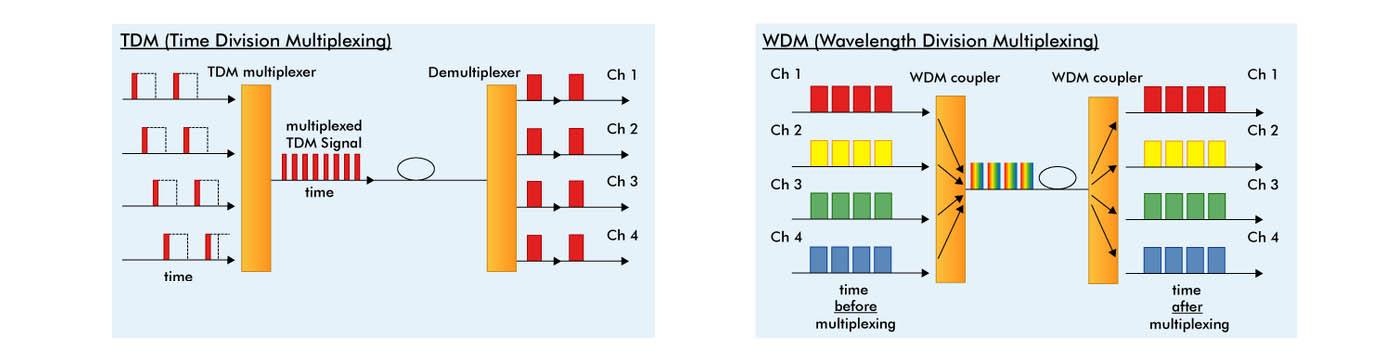
The foundation of WDM lies in the ability to send different data types over fiber networks in the form of light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
